- Community Home
- >
- Software
- >
- HPE Ezmeral: Uncut
- >
- Dealing with day 2: Practical lessons from the rea...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Dealing with day 2: Practical lessons from the real world

And it isn’t just rare events such as storms or fires you need to be prepared for. You must also plan for the entirely predictable, real-world challenges of life, such as winter weather, summer heat, and general wear-and-tear on a home.
Similarly, large-scale systems face real-world challenges. Most are predictable, and fortunately, others are rare. No matter what type of challenges you encounter, you must deal with them in practical ways to keep a system productive.
These challenges are the well-known day 2 issues. How well your system is prepared to deal with them can make a big difference in your overall operations.
It turns out that certain decisions you make ahead of time can have a particularly wide-reaching impact on your ability to deal with day 2 issues. Best practice includes: developing a comprehensive data strategy and having a unifying data infrastructure engineered for scale-efficient systems.
Properly planning for these issues is the equivalent of weatherizing your data and your enterprise. These ideas are not just aspirational. Over the last several years, I’ve talked to a lot of people with real-world experience using scale-efficient systems. I’ve detailed what I’ve learned below.
Building a scale-efficient system
A scale-efficient system is more than just a large-scale implementation. It is one that can deal with change efficiently (without costly down-time), and one that does not need to be re-architected. It’s a system built to address day 2 issues.
With that in mind, let’s dig deeper into how having a comprehensive data strategy and a unifying data infrastructure can help.
- A comprehensive data strategy
It’s imperative that enterprises consider data as an enterprise-wide asset, with the need for seamless storage, access, management and movement in on-premises data centers, cloud, and edge deployments. By looking at data requirements of a wide variety of applications that share data across the same data layer, it’s easier to maintain performance, optimize resources, and have confidence in a robust and reliable system.
- A unifying data infrastructure
A comprehensive data strategy relies on a foundation of a unifying data infrastructure rather than architecting separate systems built from point solutions. An example is the HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric, a data infrastructure engineered to meet the demands of a unified, scale-efficient system. It is a highly scalable, software-defined, and hardware agnostic data infrastructure used to store, manage, and move data from edge to data center – whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in a hybrid architecture.
A sampler of day 2 Issues: Challenges and solutions
The advantages of a scale-efficient system are widespread. Here is a sampler of the impact of such a system on a selection of day 2 issues:
- Hardware failures
In a large distributed system, hardware failure is inevitable. The question is, what is the impact on workloads and data integrity and at what cost to IT resources? HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric is a self-healing system, thanks to automatic data replication across multiple machines within a cluster combined with advanced error recovery algorithms. From the point-of-view of the application or user, a disk or machine failure is essentially invisible. Data accesses are transparently redirected by the data fabric, and existing replicas of data are re-duplicated to restore resiliency: No data loss, no workload interruptions. Additional data protection against human errors is also available thanks to data fabric snapshots, further improving business continuity.
- New applications and new tools
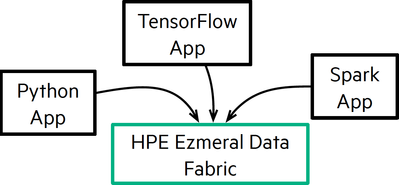
One class of day 2 problems is how to deal with the addition of new analytics and AI applications and how to use new tools or languages without having to re-architect or duplicate a large-scale system. Data fabric makes this process easy through the flexibility it offers – thanks to open, multi-API data access. Legacy applications run alongside modern applications with direct access to data stored in Ezmeral Data Fabric, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 1. Open, multi-API data access with HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric
Data fabric’s API flexibility also means that AI/machine learning models and analytics applications can, and should, run on the same system. This unified analytics approach cuts across data silos and provides a second-project advantage for high potential but speculative projects.
- Maintaining excellent performance for shared workloads
Efficient large-scale systems need to be able to adjust to the changing needs of multiple workloads. HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric automatically balances data workloads at the platform level. Additional performance enhancement occurs through optimized data locality, easily achieved with the fine-grained data placement capabilities of data fabric.
- New locations
A scale-efficient system should be able to add systems in new locations (including edge or cloud deployments) without having to re-architect. HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric works across existing and new locations, providing multiple ways to efficiently move data when needed. Built-in event streams and NoSQL database tables can be directly replicated between geo-distributed locations. Major data motion including files, tables, and streams, also can be done via mirroring with incremental updates.
In addition to moving data as needed, data fabric’s global namespace makes it possible to do remote data access. For example, a data scientist running models or doing analysis at a data center could sample data from edge locations by remote access, a particularly useful capability for large IoT systems.
Read the customer study, “Accelerating Autonomous Car Development with Ready Access to Global Data Fabric”.
- Disaster recovery plan
A major data 2 challenge is to have a reliable disaster recovery plan in place ahead of time. (Remember that hurricane?) Setting up a secondary data center at a different location is an essential part of such a plan, but how can this be done and kept updated without incurring major costs in effort and IT resources? The built-in mirroring feature of HPE Ezmeral Data Fabric with its efficient incremental updates makes this easy.
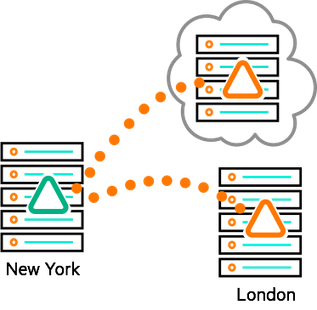
A real-world example comes from a major financial business who was new to Ezmeral Data Fabric. As part of their disaster recovery preparedness, they budgeted two weeks to copy large-scale, critical production data to a new, secondary data center. To their extreme surprise, they were able to duplicate data at the new location, carry out check sums, copy it back to the original location for verification and complete check sums – all in less than 24 hours using data fabric mirroring. That amazing result is an indicator of a truly scale-efficient system.
Ready for whatever comes next
Innovations, expansions, and unexpected events are all part of the challenges a large-scale system must weather. The combination of a unifying data infrastructure designed for flexibility and a comprehensive data strategy gives you what you need for whatever may come next.
To find out more about scale-efficient systems, watch this on-demand webinar presented by Ted Dunning and me. You can also download a free pdf of the O’Reilly ebook AI and Analytics at Scale: Lessons from Real World Production Systems.
Ellen Friedman
Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Ellen_Friedman
Ellen Friedman is a principal technologist at HPE focused on large-scale data analytics and machine learning. Ellen worked at MapR Technologies for seven years prior to her current role at HPE, where she was a committer for the Apache Drill and Apache Mahout open source projects. She is a co-author of multiple books published by O’Reilly Media, including AI & Analytics in Production, Machine Learning Logistics, and the Practical Machine Learning series.
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- SFERRY on: What is machine learning?
- MTiempos on: HPE Ezmeral Container Platform is now HPE Ezmeral ...
- Arda Acar on: Analytic model deployment too slow? Accelerate dat...
- Jeroen_Kleen on: Introducing HPE Ezmeral Container Platform 5.1
- LWhitehouse on: Catch the next wave of HPE Discover Virtual Experi...
- jnewtonhp on: Bringing Trusted Computing to the Cloud
- Marty Poniatowski on: Leverage containers to maintain business continuit...
- Data Science training in hyderabad on: How to accelerate model training and improve data ...
- vanphongpham1 on: More enterprises are using containers; here’s why.
- data science course on: Machine Learning Operationalization in the Enterpr...