- Community Home
- >
- Solutions
- >
- Tech Insights
- >
- 5G Network Slicing: the most promising 5G use case...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
5G Network Slicing: the most promising 5G use case for digital infrastructure
Part #1: This article is the first in a series of blogs on 5G network slicing and slice management.
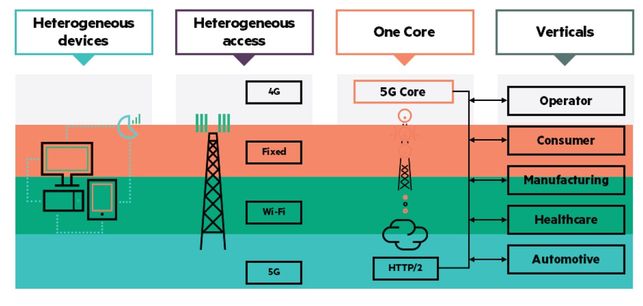
5G networks support a range of new services for consumer, government, enterprise verticals, government, and mobile virtual network operators (MVNO).
5G networks have ramped up to support a wide range of new services for consumer and enterprises, as well as MVNOs, and a number of industry verticals or government requirements. Each of these custom services has different needs, with some, like consumer mobile broadband, being grouped under the same category. Others require more specific services, for example a managed MVNO network, a highly secured government or police network, or even highly reliable low latency remote surgery services.
Figure 1: Network slicing across heterogeneous network
The network slicing concept was introduced in 2016 by NGMN . In a paper entitled “Network Slicing for 5G Networks & Services”, I helped to explain the concept of personalization of 5G services. For a target audience that included internal network managers, MVNOs, vertical industry, or end-to-end network slice instances (E2E-NSI), the paper defines a set of devices and applications with a number of policies. These terms include bandwidth, latency, geographic coverage and capabilities, that can monetize this slice, as described in a previous business paper from HPE and STL Partners.
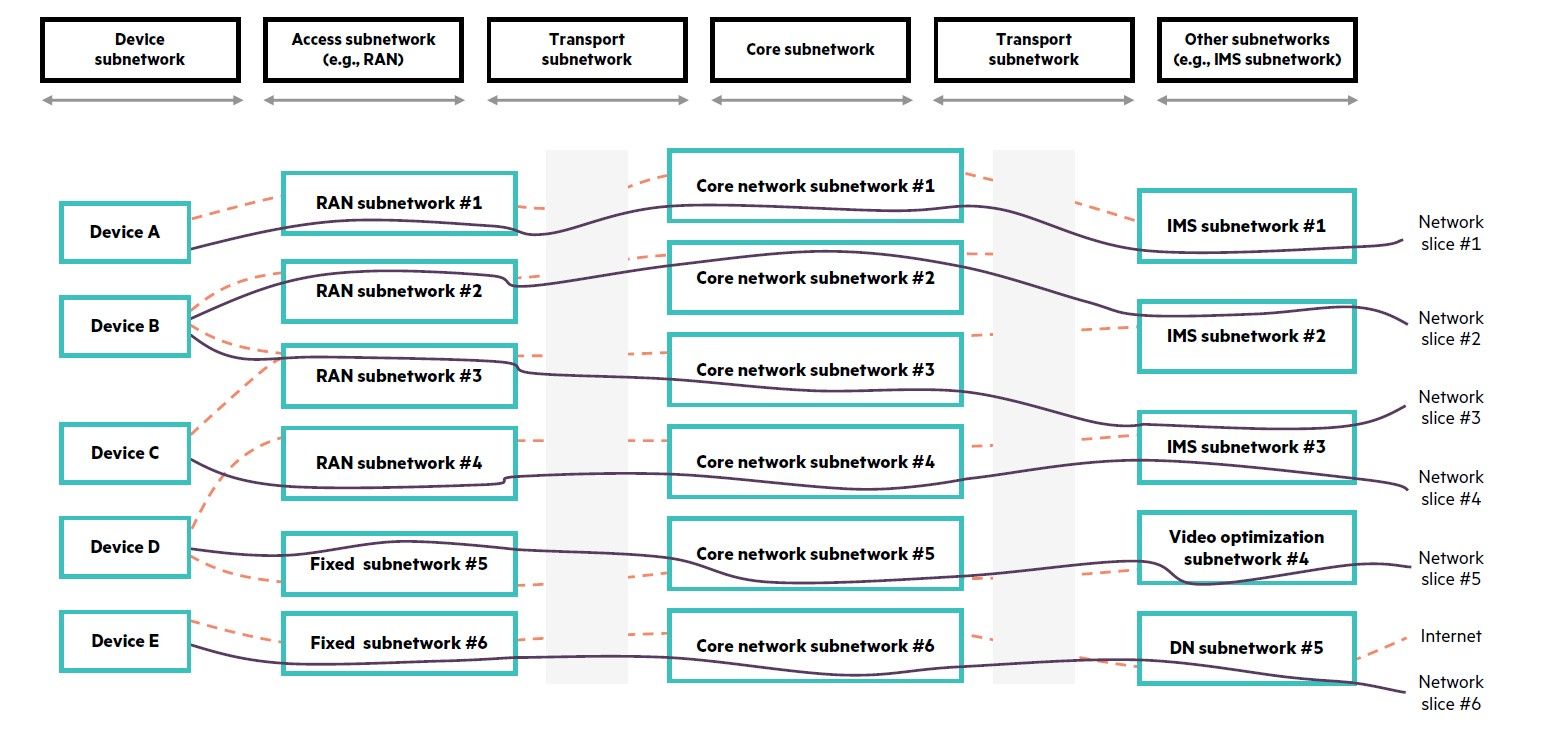
This E2E-NSI will be deployed by selecting or instantiating a combination of access, fixed and mobile, for transport and core subnetworks.
Figure 2: End-to-end network slicing
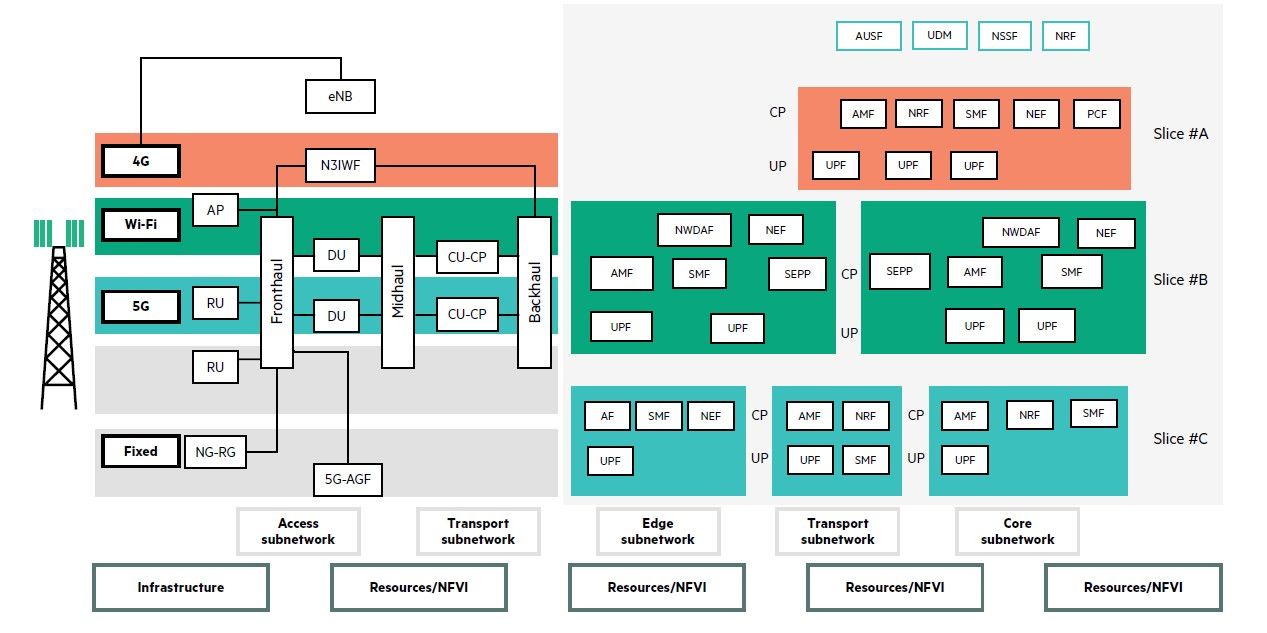
Subnetworks will be composed of two shared or dedicated network functions: physical network function (PNF) or virtual network function (VNF). For each subnetwork, an information model defines the structure of the different components. Typically the access network is composed of 4G RAN with eNB, 5G RAN with RU (Radio Unit)-DU (Distributed Unit)-CU (Centralized Unit), fixed network with NG-RG and 5G-AGF, or Wi-Fi with AP and N3IWF. Similarly, the transport network is composed of Fronthaul, Midhaul, Backhaul and WAN between the edge-core data centers.
End-to-end network slicing
Network slicing is end-to-end, including RAN and Transport network, but it also crosses multi-access, multi-domain networks, and could very likely be a multi-operator domain.
The edge and core network is composed of the 3GPP 5G Core User plane PNF (UPF) and control plane VNF (AMF, UDM, AUSF, for example) placed appropriately at the edge, or in the core, depending on placement policy or latency requirements.
Figure 3: Decomposing E2E-Network Slicing across heterogeneous network
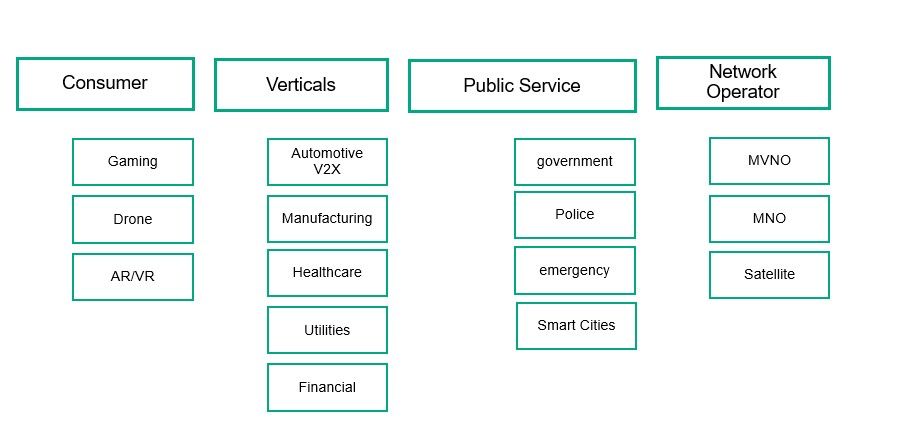
In term of use cases, the list is long. Slicing should address both consumer and enterprise services, but also government by replacing current dedicated networks, or MVNO by providing more advanced network capabilities and management control.
Figure 4 – 5G network slicing use cases
5G network slicing use cases
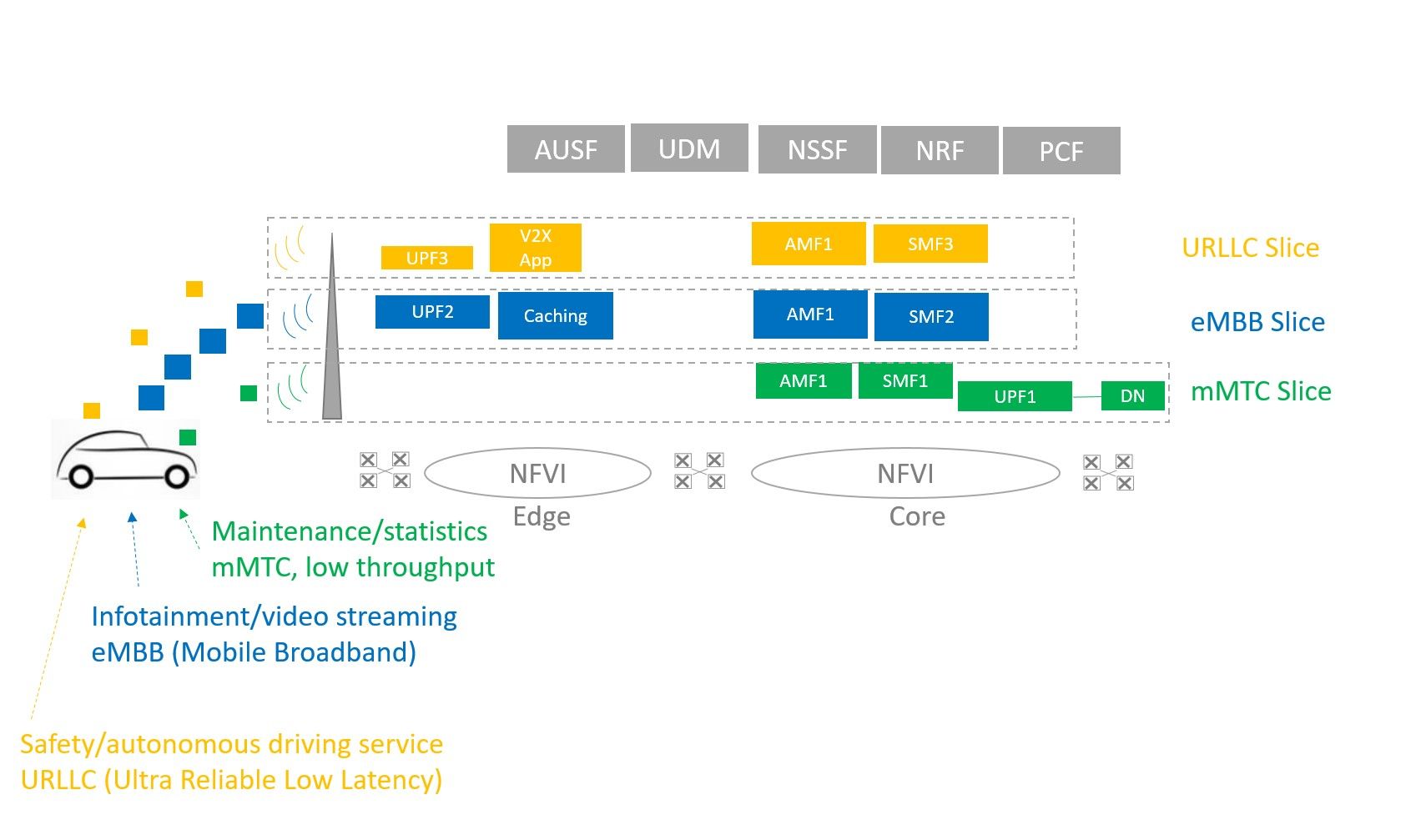
V2X is a good example of a 5G network slicing use case, with more and more connected vehicles having a mix of IoT devices like sensors, entertainment systems in the back seat requiring large bandwidth and emergency services for regulatory services or autonomous cars asking for low latency. Three categories of services that map into three set of slices are: eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband), mMTC (machine Type Communication) or uRRLC (Ultra low latency).
Figure 5: Network slicing and V2X use case
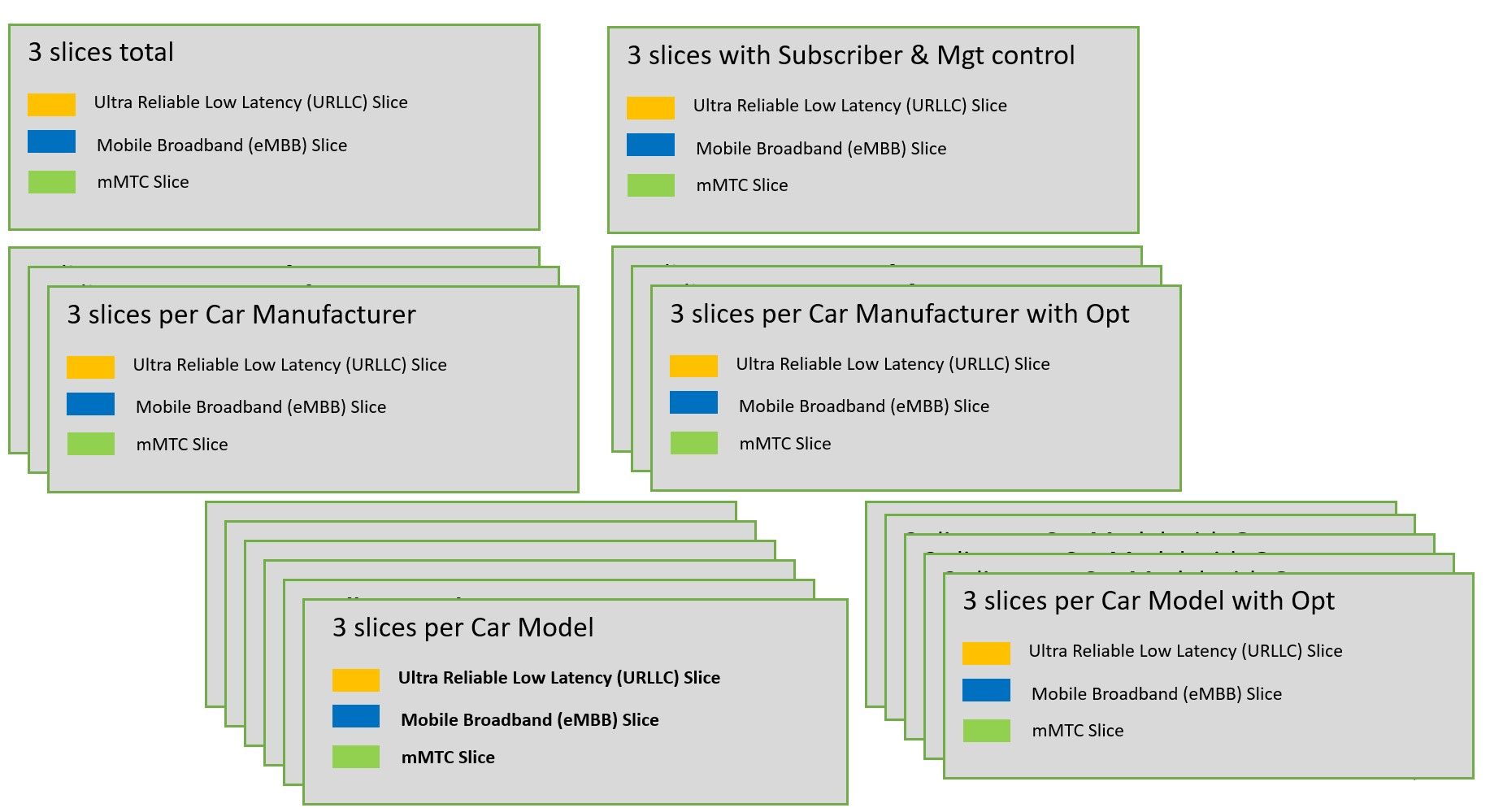
V2X is also a challenging use case in terms of the granularity of the slices. Shall operators have just 3 types of slices eMBB, mMTC and uRRLC for V2X, or more, per car manufacturer, per car models, per car options? The more slices, the more complicated it is to set up and managed -- and also to sell and support. This, however, could help meet more specific needs. Trade-offs will have to be determined case by case.
Figure 6: Network slicing granularity
Besides the business questions related to network slicing, such as business model, number of slices or dynamicity of the slices, one of the main challenges that operators have today is slice management and orchestration.
This will be the focus of our next blog. Stay tuned!
Come and Visit the HPE booth #3E11 and see our 5G Network Slicing demo
Follow HPE OSS solutions
HPE Telecommunications & CSP Solutions
HPE Intelligent Assurance datasheet
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- Amy Saunders on: Smart buildings and the future of automation
- Sandeep Pendharkar on: From rainbows and unicorns to real recognition of ...
- Anni1 on: Modern use cases for video analytics
- Terry Hughes on: CuBE Packaging improves manufacturing productivity...
- Sarah Leslie on: IoT in The Post-Digital Era is Upon Us — Are You R...
- Marty Poniatowski on: Seamlessly scaling HPC and AI initiatives with HPE...
- Sabine Sauter on: 2018 AI review: A year of innovation
- Innovation Champ on: How the Internet of Things Is Cultivating a New Vi...
- Bestvela on: Unleash the power of the cloud, right at your edge...
- Balconycrops on: HPE at Mobile World Congress: Creating a better fu...
-
5G
2 -
Artificial Intelligence
101 -
business continuity
1 -
climate change
1 -
cyber resilience
1 -
cyberresilience
1 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Edge and IoT
97 -
HPE GreenLake
1 -
resilience
1 -
security
1 -
Telco
108