- Community Home
- >
- Solutions
- >
- Tech Insights
- >
- eLAB: Moving German Electric Vehicles to the Fast ...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
eLAB: Moving German Electric Vehicles to the Fast Lane

IoT Sales Manager DACH and Russia, Hewlett Packard Enterprise

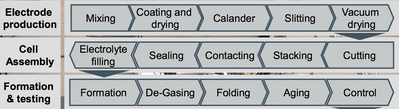
The road to IoT-connected production – labeled "Industry 4.0" in Germany – requires integration in three dimensions: a vertical one from the sensors to the ERP system, a horizontal one across the supply chain, and lifecycle integration from product development to maintenance. This can only succeed as a collaborative effort, as no organization can satisfy all requirements by itself. This is why, at eLAB, five RWTH institutes and 320+ enterprises are jointly working on digitally transforming production processes. The eLAB, designed like a factory building, allows for parallel testing of various procedures. It covers all production stages of battery manufacturing from raw materials to end-of-line testing.
eLAB covers all process steps of battery production.
Car battery production is a complex procedure involving chemical process steps as well as the interplay of mechanical and electronic components. On the data highway to the battery factory 4.0, data from various vendors’ machines needs to be collected, aggregated, and analyzed. The problem: Vendors use a variety of data formats; also, some vendors don’t allow third party data access, while in other cases, the machines don’t capture the needed data at all.
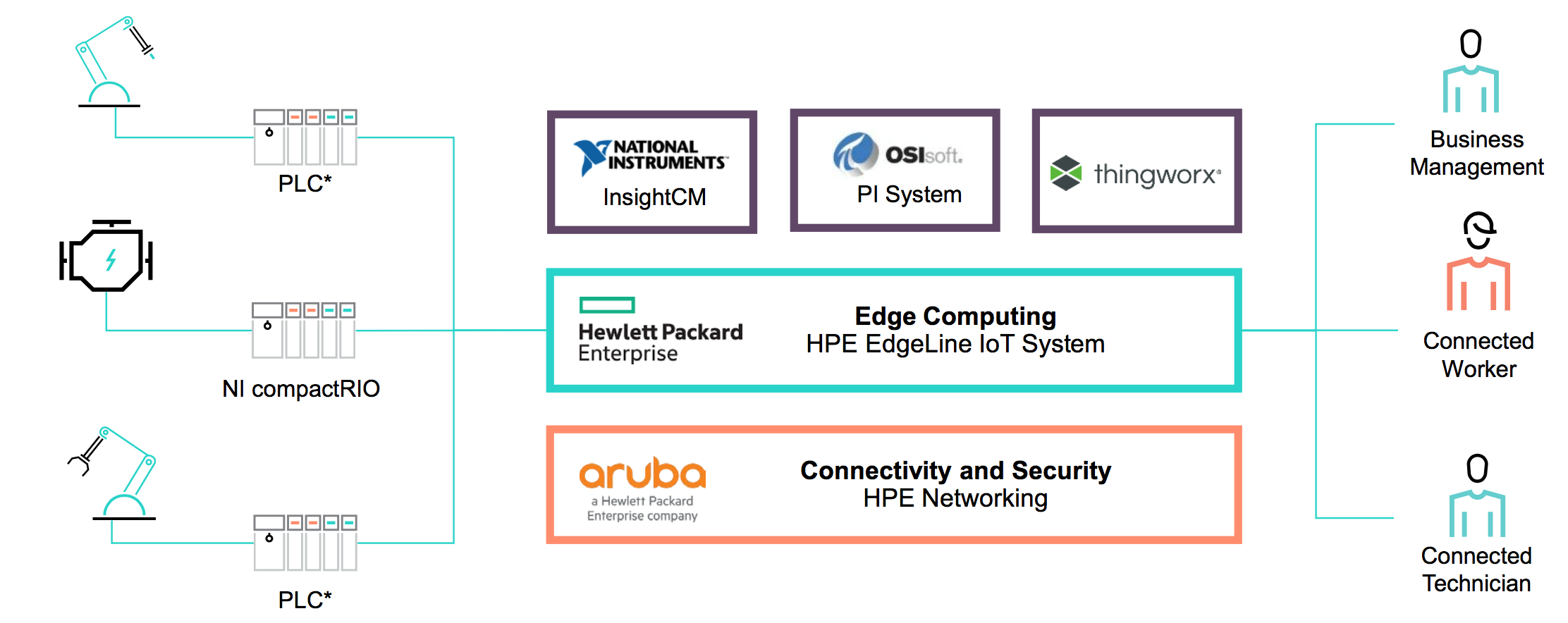
At this point, eLAB partners Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) – responsible for eLAB’s operational concepts and the integration of participating components – National Instruments, OSIsoft, and PTC enter the race: National Instruments extracts missing machine data by means of retrofitting (retroactively adding sensors to machinery). This might be a temperature sensor, or high-frequency sensor technology, e.g. for detecting fissures in coating.
Interplay of digitization solutions at RWTH Aachen’s eLAB
Data aggregation and unified data processing is done on HPE’s Edgeline systems which combine data collection, data analysis, and machine control. They provide the core platform for all services delivered by the four IT partners. Aruba networking components fast-track LAN or WLAN data transmissions, while security technology such as Aruba ClearPass provides the guard rails. OSIsoft’s PI System takes care of machine data collection, storage, and structuring. Finally, PTC’s IoT platform ThingWorx allows production line data to be analyzed, visualized, and presented via user role-specific dashboards.
A Variety of Use Cases
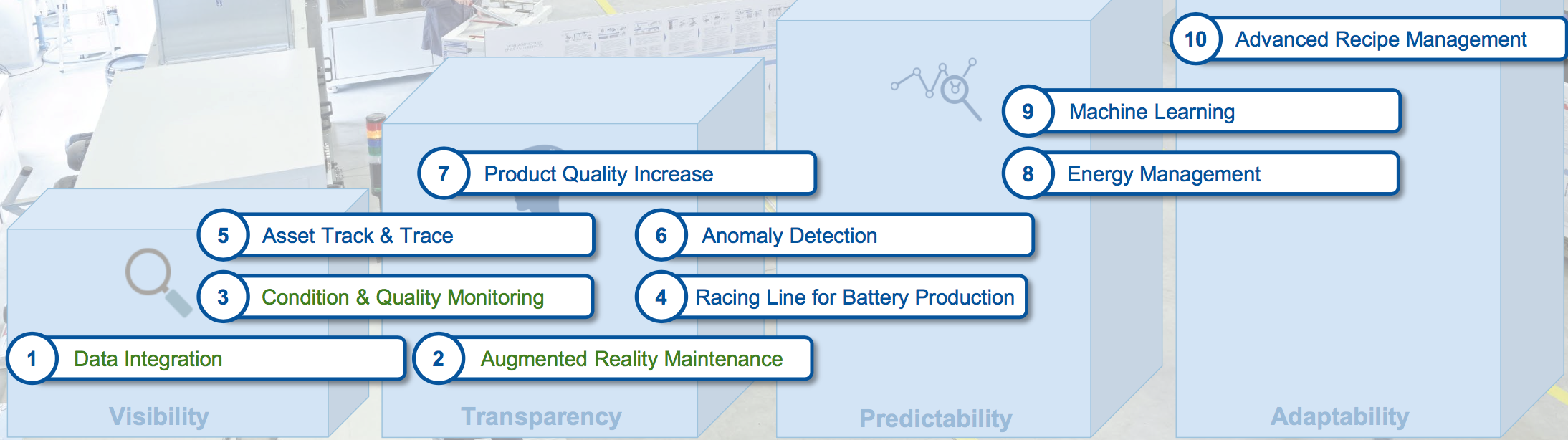
Digitization facilitates numerous use cases, from real-time monitoring to predictive maintenance. At eLAB, operational since mid-2017, three use cases have been implemented so far:
* integration of data accumulated from heterogeneous machinery,
* augmented reality- (AR-) assisted maintenance,
* condition and quality monitoring for improving battery quality, avoiding waste, and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Use cases for digitally supported battery production
At eLAB, one can, for example, have a look at augmented reality-assisted condition monitoring: Using AR glasses, the technician sees machine parameters including maintenance data, important e.g. for laser drying. With this method, electrode coating is not dried in an oven, but by means of a laser. With this occurring in a vacuum, measured parameters can only be accessed from outside. AR glasses enable a virtual view of this procedure. Additional use cases – e.g. asset tracking, energy management, and machine learning – will follow in the coming months.
eLAB demonstrates how, using the power of multi-vendor collaboration, future battery production can "put the pedal to the metal". If you want to have a look at this with your own eyes, assisted by AR glasses or not, you can do so at eLAB, or, from April 23rd to 27th, 2018 at HPE’s Hannover Messe booth (hall 6, booth A38).
If you will not be attending Hannover Messe, you can still follow the updates from the show floor in a convenient way:
- Internet of Things blog
- Infrastructure Solutions blog (in German)
- @HPE_IoT on Twitter
- @HPE_DE on Twitter (in German)
To find out how HPE can help your company collect and analyze data from connected assets, locations, and people to deliver actionable insights at the industrial edge, visit our Industrial IoT page.
To learn more about HPE’s manufacturing solutions visit www.hpe.com/info/manufacturing
Featured articles:
- Dude, where's my jetpack?
- Skills you need to survive in an IoT world
- Driverless cars need regulation. But who designs the standards?
- Want to know the future of technology? Sign up for weekly insights and resources
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- Amy Saunders on: Smart buildings and the future of automation
- Sandeep Pendharkar on: From rainbows and unicorns to real recognition of ...
- Anni1 on: Modern use cases for video analytics
- Terry Hughes on: CuBE Packaging improves manufacturing productivity...
- Sarah Leslie on: IoT in The Post-Digital Era is Upon Us — Are You R...
- Marty Poniatowski on: Seamlessly scaling HPC and AI initiatives with HPE...
- Sabine Sauter on: 2018 AI review: A year of innovation
- Innovation Champ on: How the Internet of Things Is Cultivating a New Vi...
- Bestvela on: Unleash the power of the cloud, right at your edge...
- Balconycrops on: HPE at Mobile World Congress: Creating a better fu...
-
5G
2 -
Artificial Intelligence
101 -
business continuity
1 -
climate change
1 -
cyber resilience
1 -
cyberresilience
1 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Edge and IoT
97 -
HPE GreenLake
1 -
resilience
1 -
Security
1 -
Telco
108