- Community Home
- >
- Storage
- >
- Around the Storage Block
- >
- Announcing Resource Planner, the newest HPE InfoSi...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Announcing Resource Planner, the newest HPE InfoSight Labs feature for HPE Nimble Storage
Overview
One of the most unique and cutting-edge sections of HPE InfoSight is the HPE Nimble Storage, Labs section. Here customers and partners can experiment with the next generation of intelligent storage insights powered by AI and machine learning. At HPE, data scientists are able to leverage diverse historical configuration data and performance telemetry from many HPE products. This provides an opportunity for thorough analysis of storage usage and trending as well as workload identification. We’ve been able to hone this process by utilizing the largest available data lake in the industry.
Recently published to the HPE InfoSight Labs section of the InfoSight web portal, Resource Planner helps to determine optimal workload placement based on simulated impact to Array resources and neighboring workloads. Capacity, cache and CPU needs can be predicted using the tool’s drop-down menus which represent curated application workload signatures. It helps answer these types of questions often faced by IT staff and decision makers;
- What infrastructure would be needed if I want to expand my application? Will it fit on our existing Array(s) and if not, what Array(s) should I buy?
- What infrastructure would be needed if I want to deploy a new application?
- What will the impact on current performance be if I add a certain workload on the Array ?
- How much does each workload contribute to total workload on the Array? Who are the heavy hitters?
Now with the addition of Resource Planner, HPE InfoSight can be used to answer these “what ifs”. Let’s take a closer look at some of the ways this tool can be used.
Existing workload predictions
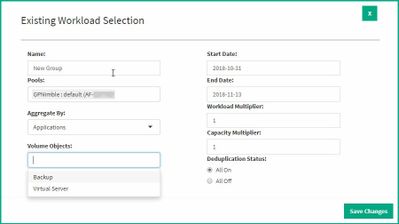
By analyzing similar workloads across many customer environments, HPE has been able to identify certain cause and effect relationships. For instance, we know what effect deduplication will have on CPU usage across different Array models. Using this type of determination, we can make changes to predict future needs for a specific set of Arrays. With Resource Planner, you can easily modify your existing workload by selecting a specific timeframe for analysis, by adding a multiplier to workload or capacity and throttle dedupe on or off. This is helpful when trying to predict if your current storage resources could handle twice the load or capacity, for example. If there are seasonal spikes in storage consumption or needs, you can select that timeframe for the workload modeling, allowing you to more accurately predict that same spike in the future on existing or new hardware.
In many cases, only certain applications or environments are expected to grow. Resource Planner also gives you the option to select one or more individual applications to simulate. This allows for very granular control of what you are modeling instead of taking the aggregated overall workload of the entire array.
Application specific analysis
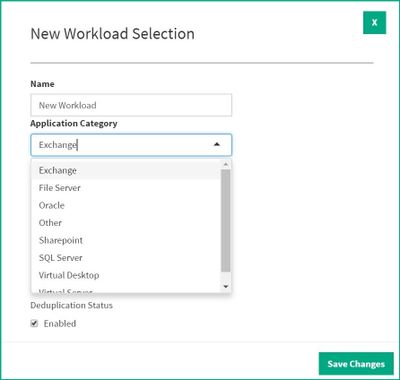
Our time-tested data science models analyze CPU, capacity and cache usage on Arrays, allowing application workload characteristics to be tagged and saved. For instance, we know that Virtual Desktop environments are more easily de-duped and compressed as compared to SQL. We know Exchange applications tend to have a higher percentage of sequential (as opposed to random) reads than Virtual Desktops. Resource Planner incorporates this kind of metadata and modeling in the Application categories available in a convenient drop-down menu.
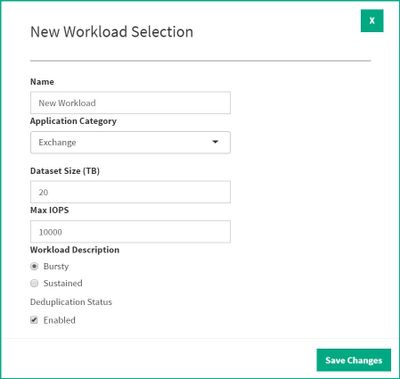
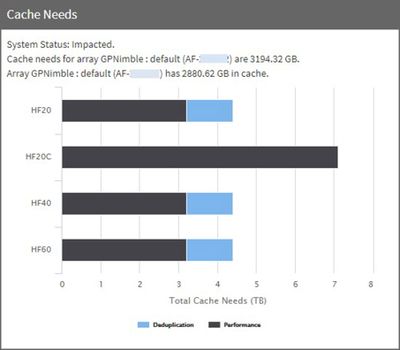
Other customizable options when adding new Application workloads are total dataset size, max IOPS, bursty or sustained workload details as well as the ability to toggle deduplication on or off. These modifications help more accurately predict capacity as well as CPU and cache needs based on characteristics provided by the HPE InfoSight analytics engine.
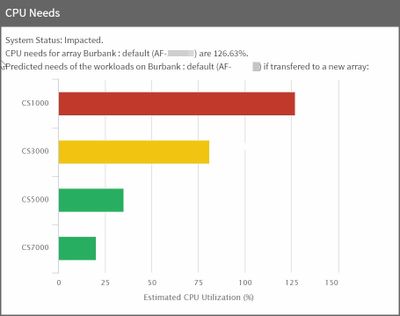
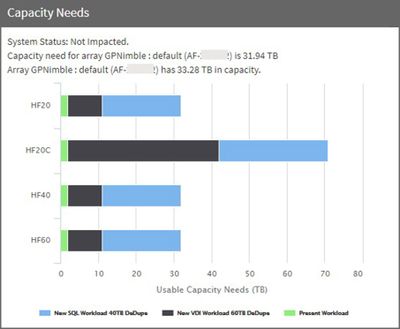
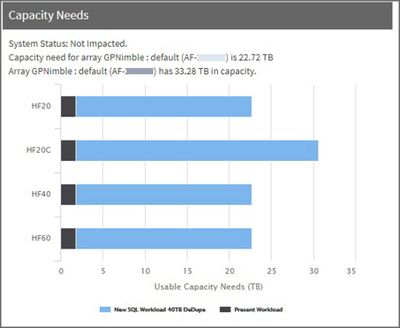
You can simulate the effects of adding or modifying applications and workloads on capacity, CPU and cache as seen across different models in the HPE Nimble Storage portfolio.
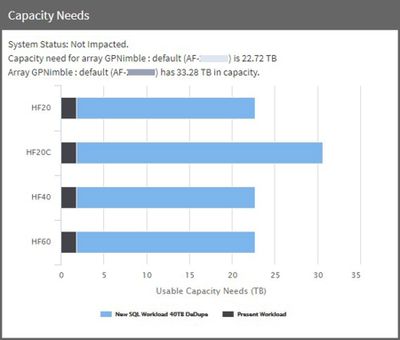
Workload distribution
Different workloads on the Array contribute to the total load. Load is calculated as an Array-wide metric. Suppose the Array is running a mix of VDI and SQL and suppose the load is 60%. How much of that 60% is from SQL? Here we see the effects of adding two different applications on an existing Array. In this example we added a VDI and a SQL application workload.
- After adding 2 new applications
- After removing the new VDI application
Conclusion
HPE InfoSight Resource Planner is a powerful tool to help customers optimize their environment and help determine if new workloads or applications can be added to their Arrays based on existing workloads. This predictive modeling can also help sales and partners accurately understand needs and properly size new purchases or upgrades. The strength of this feature is HPE’s intelligent use of the storage industry's largest data lake, strong data collection software on infrastructure components, and the way we've been able to constantly improve the data science modelling based on the range of scenarios and environments we've seen over many, many years.
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- haniff on: High-performance, low-latency networks for edge an...
- StorageExperts on: Configure vSphere Metro Storage Cluster with HPE N...
- haniff on: Need for speed and efficiency from high performanc...
- haniff on: Efficient networking for HPE’s Alletra cloud-nativ...
- CalvinZito on: What’s new in HPE SimpliVity 4.1.0
- MichaelMattsson on: HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes v1.4.0 with expanded...
- StorageExperts on: HPE Nimble Storage dHCI Intelligent 1-Click Update...
- ORielly on: Power Loss at the Edge? Protect Your Data with New...
- viraj h on: HPE Primera Storage celebrates one year!
- Ron Dharma on: Introducing Language Bindings for HPE SimpliVity R...