- Community Home
- >
- Storage
- >
- Around the Storage Block
- >
- HPE Storage Solutions for SAP HANA Dynamic Tiering...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
HPE Storage Solutions for SAP HANA Dynamic Tiering and Extension Nodes (Part 3 in 3 part series)
In my first article in this series, HPE Storage Solutions for SAP HANA Data Tiering, we saw how SAP HANA environments benefit immensely with the implementation of data tiering. In the second blog, HPE Storage Solutions for SAP HANA Native Storage Extension, we looked at how NSE helps use native storage on the HANA system for warm data. In this blog, we will talk about how HPE Storage enables you to utilize other SAP HANA tiering technologies, dynamic tiering and extension nodes.
What is SAP HANA dynamic tiering?
One of the data tiering methods employed in SAP HANA to classify, redistribute and manage hot and warm data is dynamic tiering. Dynamic tiering is a mechanism to extend SAP HANA memory with a disk-based column store called an extended store. This disk-based extended store is a storage tier with a lesser price-performance ratio.
Dynamic tiering is available as a separately licensed, add-on component to a standard SAP HANA installation. It can be deployed either on the same host as SAP HANA or on a separate host. SAP doesn’t have any stringent TDI certification requirements on the hardware used to deploy dynamic tiering. Thus, it can be deployed on commodity non-TDI certified cost-effective hardware. Dynamic tiering installs a new service in SAP HANA, called the esserver which hosts the warm data.
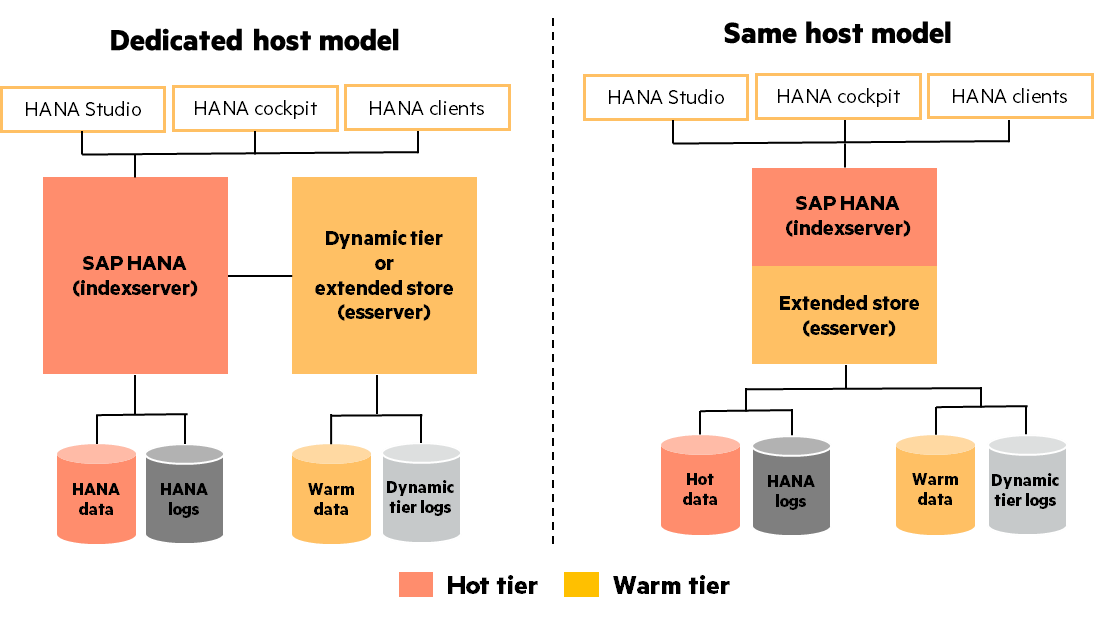
In the dedicated host deployment, warm data is hosted by a separate host called the extended worker, with esserver service hosting the warm data. However, the same host deployment holds both the hot and warm data services in the same physical host.
One of the ways to divide data into hot and warm is to create identical database schema on the hot and warm worker nodes, and then move data across based on the partitioning criterion. Otherwise, if a large table contains both hot and warm data, it can be partitioned and it can reside partially on the hot tier and partially on the warm tier. Such tables are termed as multi-store tables. Alternatively, once the warm tier is provisioned, SAP Data Lifecycle Manager in the SAP Data Warehousing Foundations can be used to create warm data criteria and warm data movement rules, and schedule them.
What is an SAP HANA extension node?
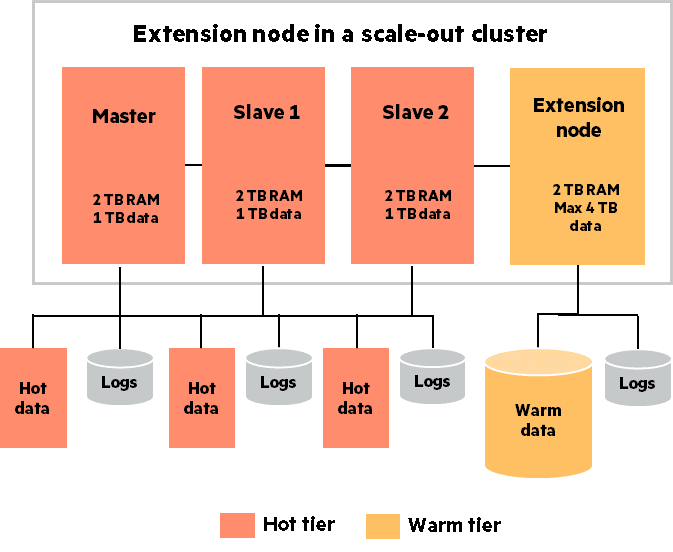
In case of SAP BW and BW/4HANA scale-out, even the warm data is expected to have almost in-memory query performance. Hence SAP has the concept of extension nodes to avail this feature. To classify, re-distribute and store warm data in a SAP HANA scale-out cluster, one node is designated as an extension node. It is a secondary worker node which is reserved for warm data storage and processing. Like all other worker nodes, an extension node has its own data and log volumes with a common NFS based shared volume.
Figure 2: SAP HANA Extension Node
The hardware used for an extension node should be TDI certified like the other worker nodes. Hence for all practical purposes, it is just another node in the scale-out cluster. The only difference is that the core-to-memory ratio which applies to a regular hot HANA node is relaxed on an extension node.
That means, RAM on an extension node can be filled with warm data beyond the usual 50% recommendation from SAP. Moreover, this node can be over-provisioned i.e. the data volume can be enlarged to store more warm data in addition to that stored in the RAM. This offers a cost-effective yet highly-performant option for storing large amounts of warm data.
HPE Storage supports both dynamic tiering and extension nodes with its leading storage products: HPE Primera, HPE Nimble, and HPE 3PAR systems. For extension nodes, it is recommended to use RAID 6 identical to that for hot data.
For more details on the implementation, sizing, and examples, please refer to the technical whitepaper I wrote or the Brighttalk session I gave on this topic.
Here is a comparison between the three SAP HANA data tiering technologies that we have seen in this series and how HPE Storage supports them:
| Features | Native Storage Extension | Dynamic Tiering | Extension Nodes |
|
Detail |
Built-in warm data store using extended storage |
SAP IQ-based, disk-based extended store |
An in-memory extension with a new worker node |
|
Warm data storage |
On disk and in buffer cache |
On disk |
In memory and on storage |
|
Hardware required |
additional storage |
Commodity hardware |
TDI certified hardware |
|
Data movement |
No physical movement of data between tiers; |
Using SQL or SAP Data Lifecycle Manager |
Using SQL or SAP Data Lifecycle Manager |
|
Licensing |
No separate license needed |
Separately licensed |
No separate license needed |
|
Technical difference from hot tier |
Warm data is loaded in the buffer cache area of main memory on request |
Warm data on esserver service |
Warm data on node with worker group as worker_dt |
|
Primary goal |
To improve price: performance ratio |
Cost savings from warm data |
High performance from warm data |
|
RAID recommendation |
SSD with RAID 6 |
HDD or SSD with RAID 6 |
SSD with RAID 6 |
|
Data protection |
HPE StoreOnce Catalyst Plug-in for SAP HANA and HPE Recovery Manager Central for data snapshots |
HPE StoreOnce Catalyst Plug-in for SAP HANA |
HPE StoreOnce Catalyst Plug-in for SAP HANA and HPE Recovery Manager Central for data snapshots |
Please do drop in a comment on how and which of these solutions fit you or your customer's SAP environment and let us know if you have any queries.
Anshul_Nagori
Meet HPE Blogger Anshul Nagori, Senior Worldwide Technical Marketing Engineer. Anshul works for the worldwide storage solutions team at HPE, and has more than 13 years of IT experience. He is a regular speaker at SAP and HPE events. His areas of focus include SAP HANA, SAS Analytics, storage, data management, and data protection solutions. Connect with Anshul on LinkedIn!
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- haniff on: High-performance, low-latency networks for edge an...
- StorageExperts on: Configure vSphere Metro Storage Cluster with HPE N...
- haniff on: Need for speed and efficiency from high performanc...
- haniff on: Efficient networking for HPE’s Alletra cloud-nativ...
- CalvinZito on: What’s new in HPE SimpliVity 4.1.0
- MichaelMattsson on: HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes v1.4.0 with expanded...
- StorageExperts on: HPE Nimble Storage dHCI Intelligent 1-Click Update...
- ORielly on: Power Loss at the Edge? Protect Your Data with New...
- viraj h on: HPE Primera Storage celebrates one year!
- Ron Dharma on: Introducing Language Bindings for HPE SimpliVity R...