- Community Home
- >
- Storage
- >
- Around the Storage Block
- >
- VMware, HPE Alletra 9000 and NVMeoF: The evolution...
Categories
Company
Local Language
Forums
Discussions
Forums
- Data Protection and Retention
- Entry Storage Systems
- Legacy
- Midrange and Enterprise Storage
- Storage Networking
- HPE Nimble Storage
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussions
Discussions
Forums
Discussions
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
- BladeSystem Infrastructure and Application Solutions
- Appliance Servers
- Alpha Servers
- BackOffice Products
- Internet Products
- HPE 9000 and HPE e3000 Servers
- Networking
- Netservers
- Secure OS Software for Linux
- Server Management (Insight Manager 7)
- Windows Server 2003
- Operating System - Tru64 Unix
- ProLiant Deployment and Provisioning
- Linux-Based Community / Regional
- Microsoft System Center Integration
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Discussion Boards
Community
Resources
Forums
Blogs
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Receive email notifications
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
VMware, HPE Alletra 9000 and NVMeoF: The evolution of Non Volatile Memory Express
Not that long ago, arrays were performance-limited by backend HDD drives. When the switch to SSD drives and All-Flash arrays occurred, this performance limitation was removed. Then, a new protocol was developed called Non Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) that was optimized for random access on solid state media over PCIe transport. The HPE Alletra 9000 is an all-NVMe array that is purpose built to exploit the benefits of NVMe and NVMe over Fabric (NVMeoF) technologies.
 NVMe over Fabric: The new gold standard
NVMe over Fabric: The new gold standard
A storage infrastructure is limited by the slowest component in the end-to-end data path – from the application on the host, to the array backend drives – and back. Not that long ago, arrays were performance-limited by the backend HDD drives. When the switch to SSD drives and all-flash arrays occurred, this performance limitation was removed. At this point everything between the application on the host and the drives in the array still ran on a SCSI protocol that was developed for HDD drives, and optimized for mechanical, serial access on magnetic spinning media.
A new optimized protocol was developed called Non Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) that was optimized for random access on solid state media over PCIe tansport, by providing a new high-performance queuing mechanism that supported 65,535 queues with 65,535 commands. The first implementations of NVMe from an array perspective were limited to SSD drives attached internally to the storage controllers. This scenario had limited benefits, as any drives external to the controllers or the data path – between the array front end and the application on the host – are still limited by the SCSI protocol. Today, NVMeoF addresses this limitation by implementing NVMe protocol over fabric technologies such as Ethernet or Fibre Channel.
The HPE Alletra 9000 is an All-NVMe array that is purpose-built to exploit the benefits of NVMeoF technologies. On the array backend, HPE Alletra 9000 uses 100 GbE running NVMEoF RoCE v2 as the transport protocol to connect to an HPE Alletra 2240 drive enclosure for capacity expansion outside the controller enclosure. This increases performance with better CPU utilization and capacity, by leveraging external drive enclosure expansion.
On the HPE Alletra 9000 front end, an out-to-the-application at the host SCSI will be replaced with the NVMeoF FC protocol. The reasons for starting with NVMeoF FC? It is easier to setup and has wider interoperability support – plus Gen 6 FC has a low barrier of entry – with only a software update required for a large installed base. By untilizing the VMWare ESXi 7.0 U2, HPE Alletra 9000 running the 9.4 code and NVMeoF FC, the remaining dependence on the SCSI protocol is removed.

VMware is a great place to start the migration to NVMeoF
In order to a achieve an all NVMe/NVMeoF environment – in addition to having an all NVMe array – you need to make sure that the SAN Fabric, host HBAs, and host operating systems are all NVMeoF capable. Migrations of this type do not happen overnight, but knowing what is or is not supported, allows for an easier conversion to NVMEoF and its benefits, as your infrastructure is refreshed and updated.
Many of our joint customers have large VMware infrastructures in their data centers, and this gives us a great place to start, with VMware ESXi 7.0 U2 support for NVMeoF, when HPE Alletra 9000 running code level 9.4 is launched. As with any new functionality, additional support will be added over time.
Below is a snapshot of the current functionality from a VMware point-of-view.
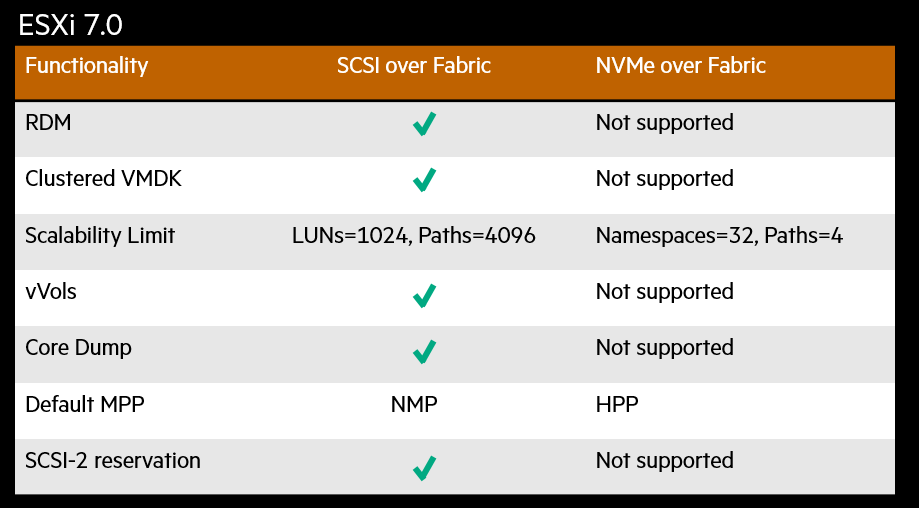
As this is the first release of NVMeoF FC – just like at the operating system level – there are array features that still work using the standard FCP (SCSI) protocol but are not yet supported with NVMeoF FC.
Below is a summary of this status in the first release. Support for these features will be added in future releases.
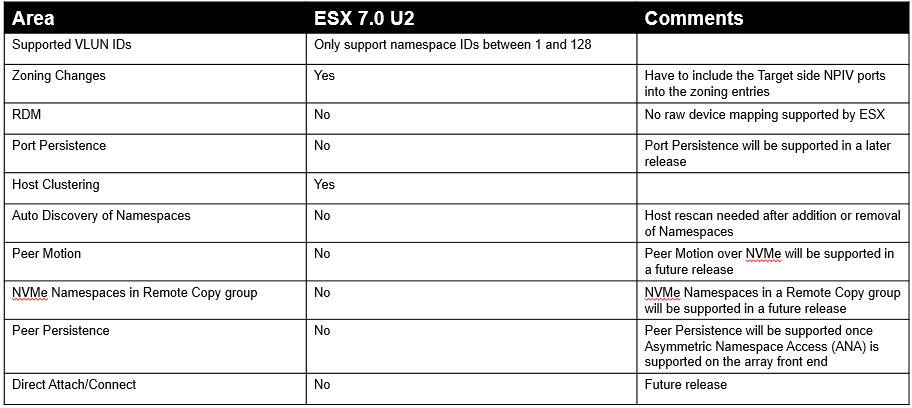
Benefits of an end-to-end NVMeoF data infrastructure
The entire storage market is racing towards a new type of data infrastructure based on new technologies like AFA, NVMe, and NVMeoF. Customers are looking for features like hybrid cloud, and the ability to consume these features as-a-service in these environments. In these scenarios connectivity is key. The old SCSI-based protocols like FC and iSCSI will not keep up, so updated protocols based on NVMe – including NVMeoF FC and the Ethernet-based protocols like TCP and RoCE v2 – will provide this robust connectivity.
The best way to understand the real benefits of NVMeoF FC over FCP is to look at a comparison of the per-port performance capabilities. With NVMeoF, you have more efficient drivers for the HBAs which results in lower CPU utilization on the storage controllers, resulting in better system scalability. This means that maximum performance levels can be achieved with fewer ports, so the benefits will be instantly seen in small block workloads.
The following figure is an example of this performance comparison. At an individual port level, you get much lower latency with NVMeoF than FCP, at maximum throughput or much higher throughput, at the same latency.
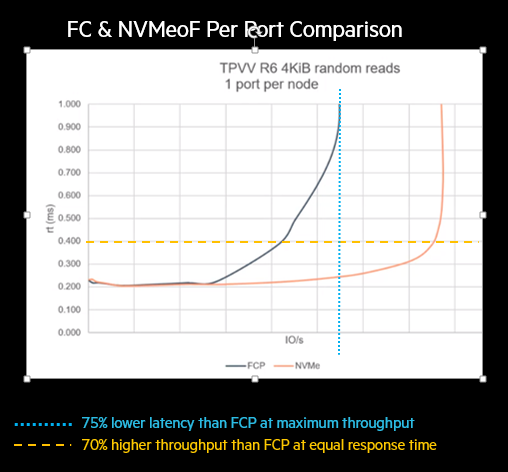
All of the generation 6 and 7-B and C series FC switches support NVMeoF. Also, all of the current HBA adapters support NVMeoF.
See the switch and HBA products available in the diagram below. When the additional Ethernet-based options like TCP become available, HPE has a full line of Ethernet storage networking products available.
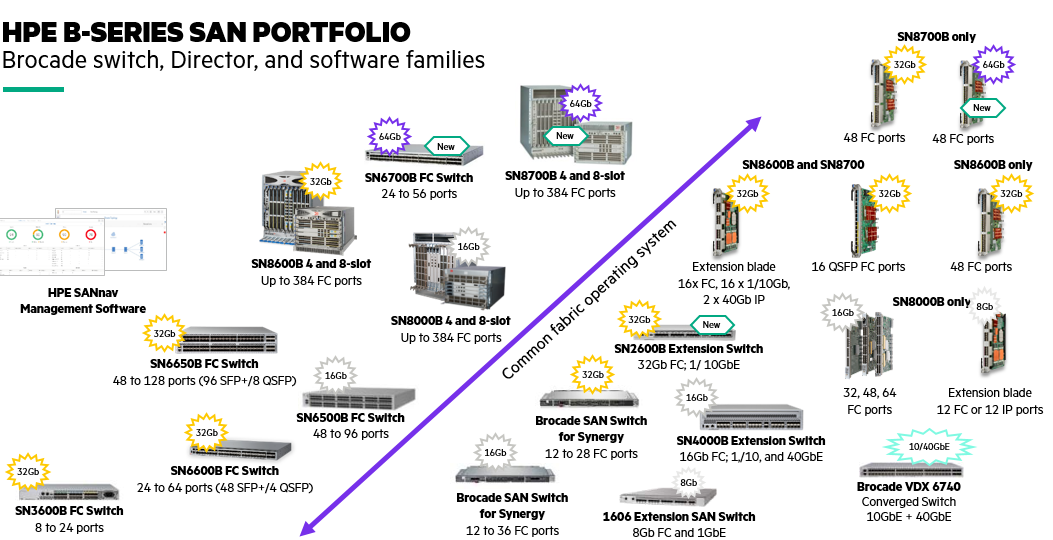
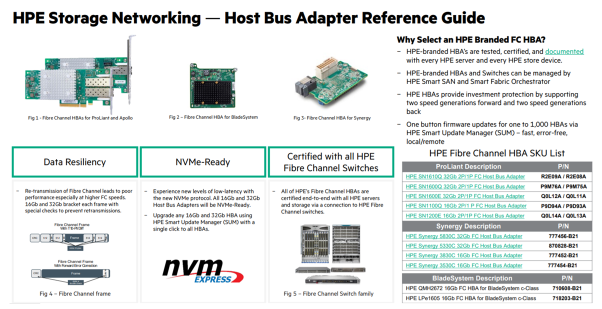
With HPE Alletra 9000 running 9.4 code, HPE offers everything your business needs for an end-to-end AFA, NVMe and NVMeoF solution – from the application/host to the array backend – and back. This gives you all of the host and array HBA ports to support both FCP and NVMeoF protocols at the same time, and facilitates the phased migration as refreshes are performed, or application workloads demand it.
For more information on HPE Storage Networking, please check out our Storage Networking Solutions page.
For more information on HPE B-Series Switches, check out our online store.

Storage Experts
Hewlett Packard Enterprise
twitter.com/HPE_Storage
linkedin.com/showcase/hpestorage/
hpe.com/storage
- Back to Blog
- Newer Article
- Older Article
- haniff on: High-performance, low-latency networks for edge an...
- StorageExperts on: Configure vSphere Metro Storage Cluster with HPE N...
- haniff on: Need for speed and efficiency from high performanc...
- haniff on: Efficient networking for HPE’s Alletra cloud-nativ...
- CalvinZito on: What’s new in HPE SimpliVity 4.1.0
- MichaelMattsson on: HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes v1.4.0 with expanded...
- StorageExperts on: HPE Nimble Storage dHCI Intelligent 1-Click Update...
- ORielly on: Power Loss at the Edge? Protect Your Data with New...
- viraj h on: HPE Primera Storage celebrates one year!
- Ron Dharma on: Introducing Language Bindings for HPE SimpliVity R...


